Know Your Body
We must know that how diabetes affects our body. The better we know, the better we can analyze our condition.
What is Diabetes?
- In diabetes, blood glucose levels rise abnormally that result from defects in insulin secretion or the body's ability to use insulin.
- This metabolism syndrome is also known as hyperglycemia as it causes high levels of glucose in blood.
- Following is the pathway for glucose metabolism (Glucose homeostasis)
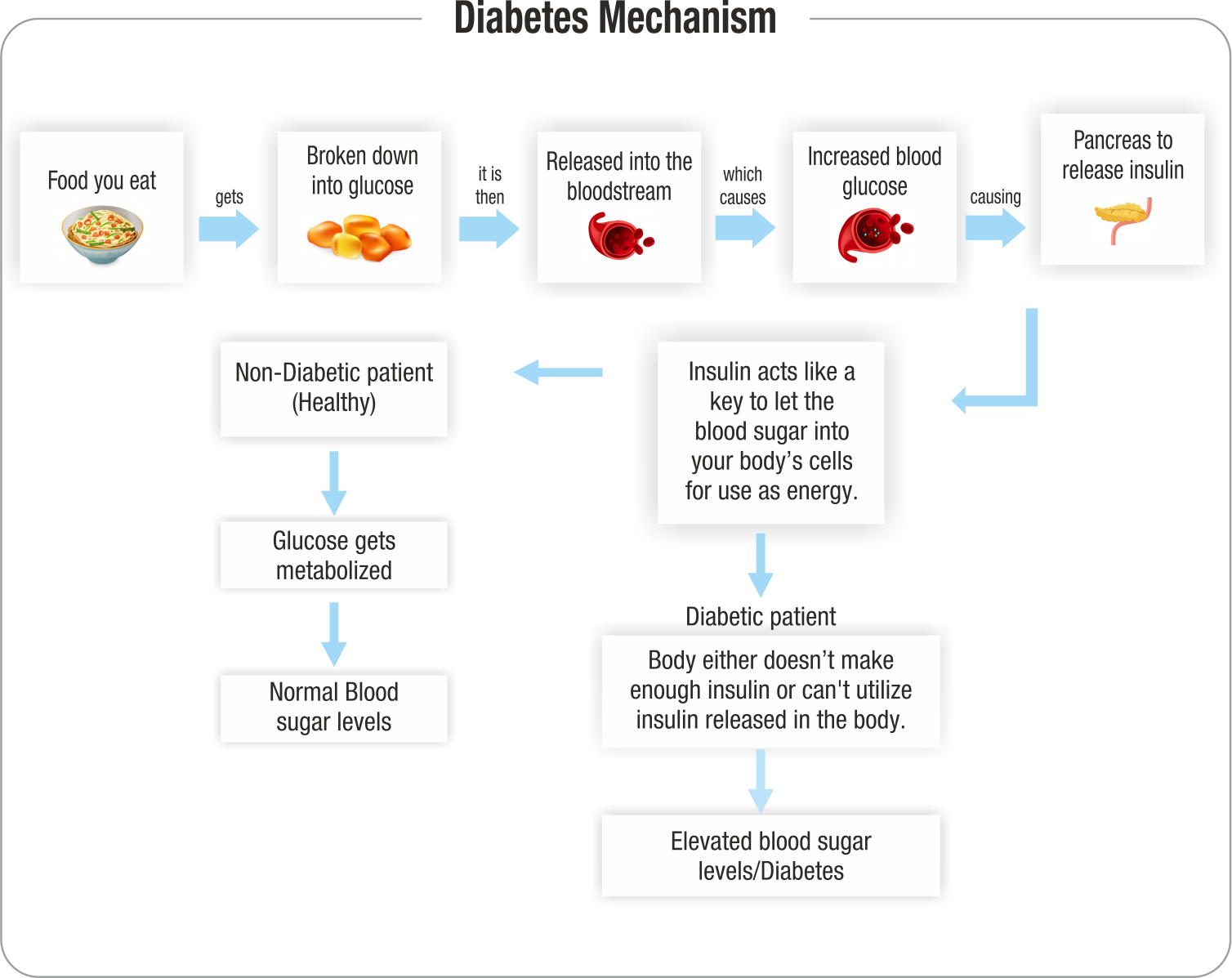
Types of Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes
- The pancreas cannot produce insulin. It is caused by an autoimmune reaction (the body attacks itself by mistake) that stops body from making insulin.
- It can only be manages by insulin injections.
Type 2 diabetes
- It is also called as T2DM (Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus)
- In T2DM body either does not produce insulin or insulin sensitivity is reduced.
- It develops over many years and is usually diagnosed in adults.
Gestational diabetes
- It develops in pregnant women who have never had diabetes.
- Usually goes away after childbirth but increases risk of obesity & type 2 diabetes later in child's life.
Symptoms
The symptoms of diabetes can be mild or absent and hence, it goes undiagnosed for years. The major symptoms of diabetes are characterized by 3Ps.
Polydipsia
Drinking plenty of water will usually take care of your thirst. But sometimes, no amount of water seems like enough. You'll drink and drink and drink -- and drink -- and still be thirsty. That's polydipsia.
Polydipsia is a medical name for the feeling of extreme thirstiness. Polydipsia is often linked to urinary conditions that cause you to urinate a lot. This can make your body feel a constant need to replace the fluids lost in urination. It can also be caused by physical processes that cause you to lose a lot of fluid.

Polyphagia
Polyphagia is not a disorder by itself, rather it is a symptom indicating an underlying medical condition. It is frequently a result of abnormal blood glucose levels.
Polyphagia, also known as hyperphagia, is the medical term for excessive or extreme hunger. It's different than having an increased appetite after exercise or other physical activity. While your hunger level will return to normal after eating in those cases, polyphagia won't go away if you eat more food.
Polyuria
Polyuria is excessive or an abnormally large production or passage of urine. Increased production and passage of urine may also be termed diuresis.
Polyuria is a condition where the body urinates more than usual and passes excessive or abnormally large amounts of urine each time you urinate. Polyuria is defined as the frequent passage of large volumes of urine - more than 3 litres a day compared to the normal daily urine output in adults of about 1 to 2 litres.

Others
Apart from 3Ps following symptoms may also occur:
- Weakness
- Blurry vision
- Nausea
- Slow healing of cuts

Risk Factors
Mentioned below are possible causes of T2DM

Unhealthy Diet
Possible cause of T2DM include consuming fast food can increase cholesterol resulting in increased risk.

Family history of diabetes
Your risk increase if a parent or sibling has T2DM

Physical inactivity
The less active you are, the greater you are at risk of T2DM

Ethnicity
Although its unclear why, people of certain races are at high risk
High blood pressure
Having BP over 140/90mm Hg is linked to an increased risk
Overweight
The more fatty tissues you have, the more resistant your cells become to insulin

Impaired glucose tolerance (IGT)
IGT indicates that blood glucose is raised beyond normal level, increasing the risk of CVD & Diabetes
Diagnosis Methods
Following tests are usually performed for diagnosing diabetes:
-
Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c)
- Also known as gylcated haemoglobin
- It is an average of blood glucose over the past 2 or 3 months
- It is the most important test to confirm hyperglycaemia in patients and to observe how well diabetes is controlled
- It can be performed in laboratory or HbA1c machine
-
Fasting plasma glucose (FPG)
- This is also known as fasting blood sugar test
- It measures blood sugar on an empty stomach
- This test is performed before eating or drinking anything except water for 8 hours before the test
- FPG is performed using a glucometer, therefore also known as glucometer test
-
Oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT)
- This checks blood glucose before and 2 hours after drinking 8 ounces of a syrup glucose solution that contains 75 grams of sugar to see how the body handles the sugar
- OGTT is performed in laboratory
Diagnostic Parameter Stages
| Parameters | Normal | Prediabetes | Diabetes |
| FPG | <100 mg/dL (<5.6 mmol/L) |
100-125 mg/dL (5.6-6.9 mmol/L) |
>=126 mg/dL (>=7.0 mmol/L) |
| OGTT | <140 mg/dL (<7.8 mmol/L) |
<140 mg/dL (7.8-11.0 mmol/L) |
>=200 mg/dL (>=11.1 mmol/L) |
| HbA1c | <5.7% | 5.7% - 6.4% | >=6.5% |
